Endpoint sinks innovate the risk factors of COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), referred to as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, is listed as the four major chronic diseases in the world by the World Health Organization together with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and cancer. According to the 2019 Global Health Estimate Report released by the World Health Organization, COPD has become the third leading cause of death after ischemic heart disease and stroke, accounting for 6% of the total number of deaths worldwide. What are the pathogenic factors of such a terrible chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? Let’s learn about the risk factors of COPD together.
The main risk factors of COPD include smoking, environmental pollution, occupational dust and chemical contact, infection, genetic factors and so on.
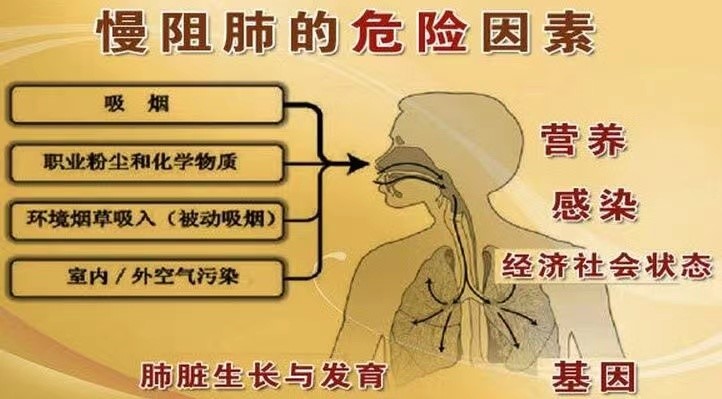
Figure 1 comes from QQ browser Zhejiang Online.
I. Smoking and environmental factors
1. Smoking:
Smoking is the most common risk factor for COPD at present. Compared with non-smokers, smokers are more likely to have respiratory symptoms and abnormal lung function. The risk of smokers suffering from COPD is related to the amount of smoking. The age of starting smoking, the total number of smoking packages and smoking status are all predictive factors of COPD mortality. Many studies have made it clear that smoking is the most important risk factor for the occurrence and development of COPD, and the increase of smokers will inevitably lead to the increase of COPD population. Smoking index (the product of the number of cigarettes per day and the number of years of smoking) is more than 200 years, which is obviously harmful. The longer you smoke, the more you smoke every day, and the higher the prevalence of COPD. The survey of coal miners also shows that the higher the smoking index, the higher the proportion of coal miners’ pneumoconiosis complicated with COPD.
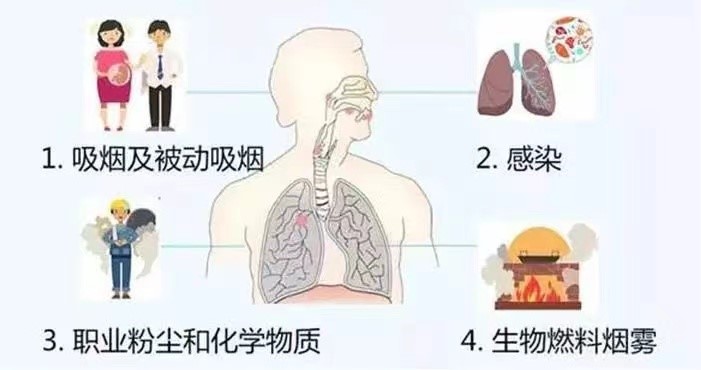
Figure 2 comes from QQ browser Sohu.com.
2, occupational dust and chemicals:
Occupational exposure is an easily overlooked risk factor for COPD, including mining, quarrying, cement dust, foundry, grain dust, paint, chemical industry and other occupational dust or gas smoke exposure. With the development of social industrialization, irritating smoke, dust and air pollution (such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, chlorine gas and ozone) are becoming more and more serious. These factors can induce COPD and make the existing COPD chronic.
3. Air pollution:
Air pollution is one of the important factors leading to COPD. The air pollution in cities and towns is mainly caused by the burning of petroleum, which mainly comes from the tail gas emitted by motor vehicles. Its main components are carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, soot particles (some heavy metal compounds, lead compounds, black smoke and oil mist), formaldehyde and so on. Indoor air pollution is also an important factor leading to COPD in many developing countries, especially women in developing countries.

Figure 3 comes from QQ browser mobile phone Sohu.
4. Infection:
More than 10 kinds of virus infections are related to chronic bronchitis. Influenza virus, rhinovirus and coronavirus can all cause upper respiratory tract infection.
Figure 4 comes from QQ browser Australian network.
Second, host factors There are genetic susceptibility genes in COPD patients.
1, airway high reactivity:
Airway hyperresponsiveness, which is closely related to heredity, is considered to be related to COPD.
2, lung development and poor growth:
According to foreign research data, individuals who suffer from poor lung development or growth during pregnancy, newborn, infancy or childhood are prone to COPD in adulthood.
3. Family aggregation tendency:
COPD has a genetic tendency. It is clear that COPD is a hereditary disease, but its genetic tendency is not as high as asthma.
Third, other factors: including gender and age, socio-economic status and malnutrition.
COPD can be prevented, but it can’t be cured at present. Patients with COPD are usually diagnosed to be over 40 years old. Xiaobian here suggests that people over 40 years old, those who have been exposed to risk factors such as long-term smoking, occupational dust and chemical substances, should be tested for lung function every year.
Content source:
[1] Xiao Jian, Du Chunling. Research progress on etiology and pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. China Journal of Gerontology, 2014,34(11):3191-3194.
From Weibo Chuanbei Medical Young Volunteers Association; From Weibo Sanlian Life Weekly; From sogou encyclopedia.